Scope
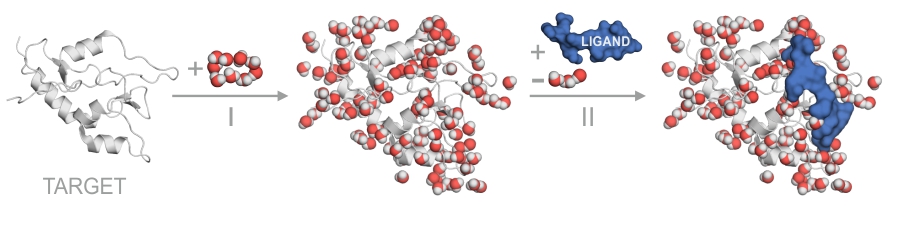
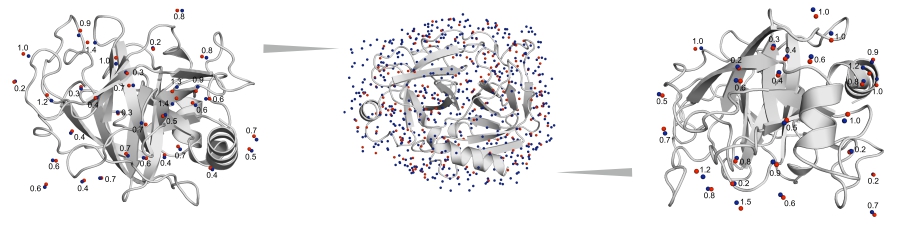
MobyWat is a program for calculation of hydration structures and networks of molecular surfaces and interfaces. The program uses a series of frames from molecular dynamics simulations. MobyWat has been thoroughly tested on protein surfaces and target-ligand interfaces, and can be recommended for experimental or theoretical investigations dealing with hydration problems. Possible applications may include but are not restricted to the following projects.
-
Refinements and analyses of hydration structure assigned by crystallography.
-
Prediction of hydration structure at problematic (overlapping, non-defined) regions of the density map.
-
Prediction of hydration structure of solute molecules such as proteins or their complexes measured by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
-
Building hydration structure around homology modeled proteins and other modeled molecules or surfaces.
-
Selection of structural water molecules for calculation of binding strength between molecular partners of complexes.
-
Selection of surface-bound water molecules stabilizing protein structure.
-
Selection of conserved water molecules.
-
Estimation of local density and mobility of the hydration structure.
-
Prediction, analysis, and categorization of hydration networks.